- TB Enterprise - Place Where Ideas Convert Into Creation.
- +91-9067176874
- info@tbenterprise.in
Indoor Air Quality


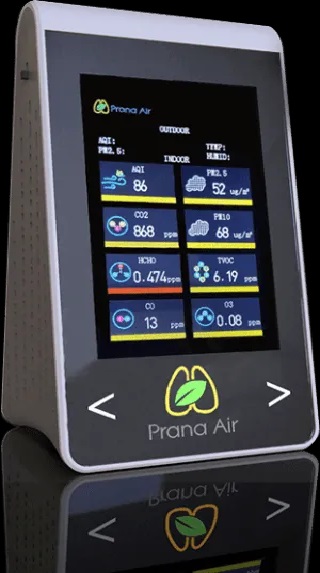
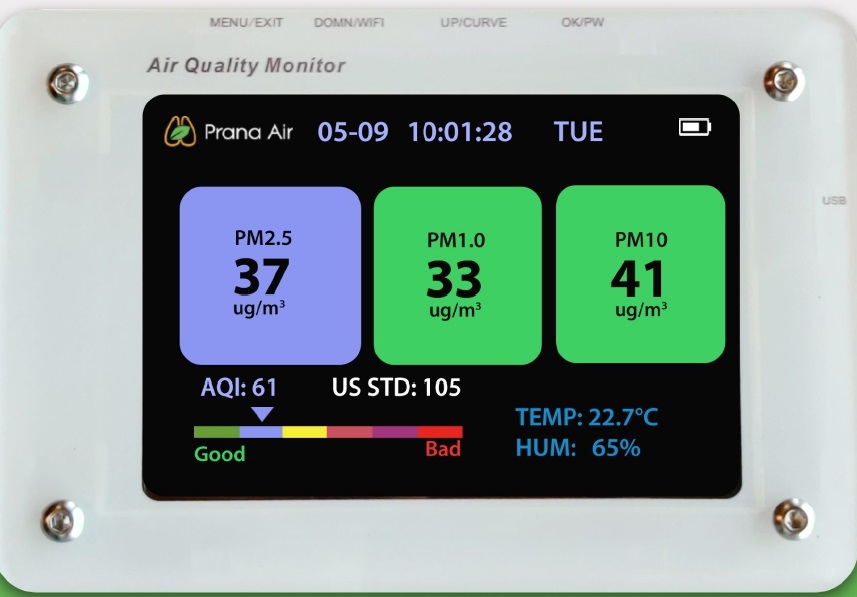

indoor air quality –
Indoor air quality refers to the quality of the air inside buildings and structures, including homes, offices, and schools. It is important to maintain good indoor air quality as poor air quality can have negative effects on our health and well-being.
- Importance of indoor air quality for health and well-being –
The importance of indoor air quality for health and well-being cannot be overstated. Poor air quality can lead to a variety of health issues, ranging from respiratory problems to allergies and even more serious conditions such as asthma and lung cancer. In fact, the World Health Organization estimates that around 4.3 million people die prematurely every year due to indoor air pollution.
- Thesis statement: Improving indoor air quality is crucial for maintaining a healthy and comfortable indoor environment. –
There are several factors that contribute to poor indoor air quality, including inadequate ventilation, the presence of pollutants such as tobacco smoke and chemicals, and the buildup of allergens like dust mites and pet dander. These pollutants can accumulate in indoor spaces and have a detrimental impact on our health. Therefore, it is essential to take proactive measures to improve indoor air quality and create a safe and healthy living environment for ourselves and our loved ones.
Factors Affecting Indoor Air Quality –
There are several factors that can affect indoor air quality. One of the main factors is inadequate ventilation, which can lead to a buildup of pollutants and stale air. Without proper ventilation, these pollutants can become trapped inside, increasing the risk of respiratory issues and other health problems. Another factor is the presence of specific pollutants, such as tobacco smoke and chemicals from cleaning products or building materials. These pollutants can release harmful particles and gases into the air, which can be inhaled and cause irritation or even long-term health issues.
Sources of indoor air pollution (e.g., chemicals, biological contaminants, combustion byproducts) –
can come from a variety of sources within the home. Chemicals from household cleaners, paints, and solvents can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air, which can contribute to respiratory problems and allergic reactions. Biological contaminants, such as mold, bacteria, and viruses, can thrive in damp or poorly ventilated areas and can cause respiratory infections and other health issues. Combustion byproducts from gas stoves, fireplaces, and tobacco smoke can release carbon monoxide and other harmful gases, posing a serious risk to indoor air quality.
- Common indoor air pollutants and their health effects –
include formaldehyde, which can irritate the eyes, nose, and throat, and is classified as a carcinogen. Another common pollutant is radon, a radioactive gas that can seep into homes from the ground and increase the risk of lung cancer. Additionally, secondhand smoke from cigarettes contains thousands of chemicals, many of which are known to cause cancer and respiratory problems. These pollutants and their health effects highlight the importance of maintaining good indoor air quality to protect our respiratory health.
- Poor ventilation as a contributing factor to indoor air pollution –
Poor ventilation is a major contributing factor to indoor air pollution. When a building is not properly ventilated, pollutants can become trapped inside, leading to a buildup of harmful substances. Without fresh air circulating, pollutants like dust, allergens, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can accumulate to high levels, posing a serious risk to our health. Inadequate ventilation can also lead to increased humidity levels, which can promote the growth of mold and mildew, further exacerbating respiratory problems. Therefore, ensuring proper ventilation is crucial in maintaining good indoor air quality and protecting our respiratory health.
Health Effects of Poor Indoor Air Quality –
Poor indoor air quality can have a significant impact on our overall health. Exposure to high levels of pollutants can lead to a range of health issues, including respiratory problems, allergies, and even more serious conditions such as asthma and lung cancer. Additionally, poor indoor air quality has been linked to headaches, fatigue, and decreased cognitive function.
- Respiratory problems (e.g., asthma, allergies, infections) –
Respiratory problems are one of the most common health effects of poor indoor air quality. When we breathe in polluted air, it can irritate and inflame our respiratory system, leading to symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. For individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions like asthma, exposure to indoor air pollutants can trigger or worsen their symptoms. Furthermore, prolonged exposure to poor indoor air quality can increase the risk of developing respiratory infections, as the pollutants weaken the immune system’s ability to fight off pathogens.
- Headaches, dizziness, and fatigue –
are also common symptoms associated with poor indoor air quality. These symptoms can be caused by the presence of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which are released from various household products such as cleaning agents, paints, and furniture. VOCs can have both short-term and long-term health effects, with prolonged exposure increasing the risk of developing chronic illnesses such as respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, poor indoor air quality can also have detrimental effects on cognitive function and mental health. Studies have shown that high levels of indoor air pollutants can impair concentration, memory, and decision-making abilities, leading to decreased productivity and overall
Strategies for Improving Indoor Air Quality –
include regular cleaning and maintenance of HVAC systems, proper ventilation to allow for fresh air circulation, and minimizing the use of products that release harmful chemicals into the air. It is also important to regularly clean and vacuum carpets, as they can trap dust, allergens, and other pollutants. Using air purifiers and keeping indoor humidity levels in check can further contribute to better indoor air quality. Additionally, promoting a smoke-free environment and avoiding the use of harsh cleaning chemicals can greatly reduce indoor air pollution. By implementing these strategies, individuals can create a healthier and safer indoor environment for themselves and their loved ones.
- Proper ventilation and air circulation –
is another crucial factor in maintaining good indoor air quality. Opening windows and doors regularly to let fresh air in can help remove stagnant air and improve ventilation. Installing exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens can also help remove excess moisture and prevent the growth of mold and mildew. Furthermore, using ceiling fans and portable fans can help circulate the air, preventing the buildup of pollutants in specific areas of the house. By ensuring proper ventilation and air circulation, individuals can greatly enhance the overall air quality in their homes.
Technologies and Tools for Monitoring Indoor Air Quality
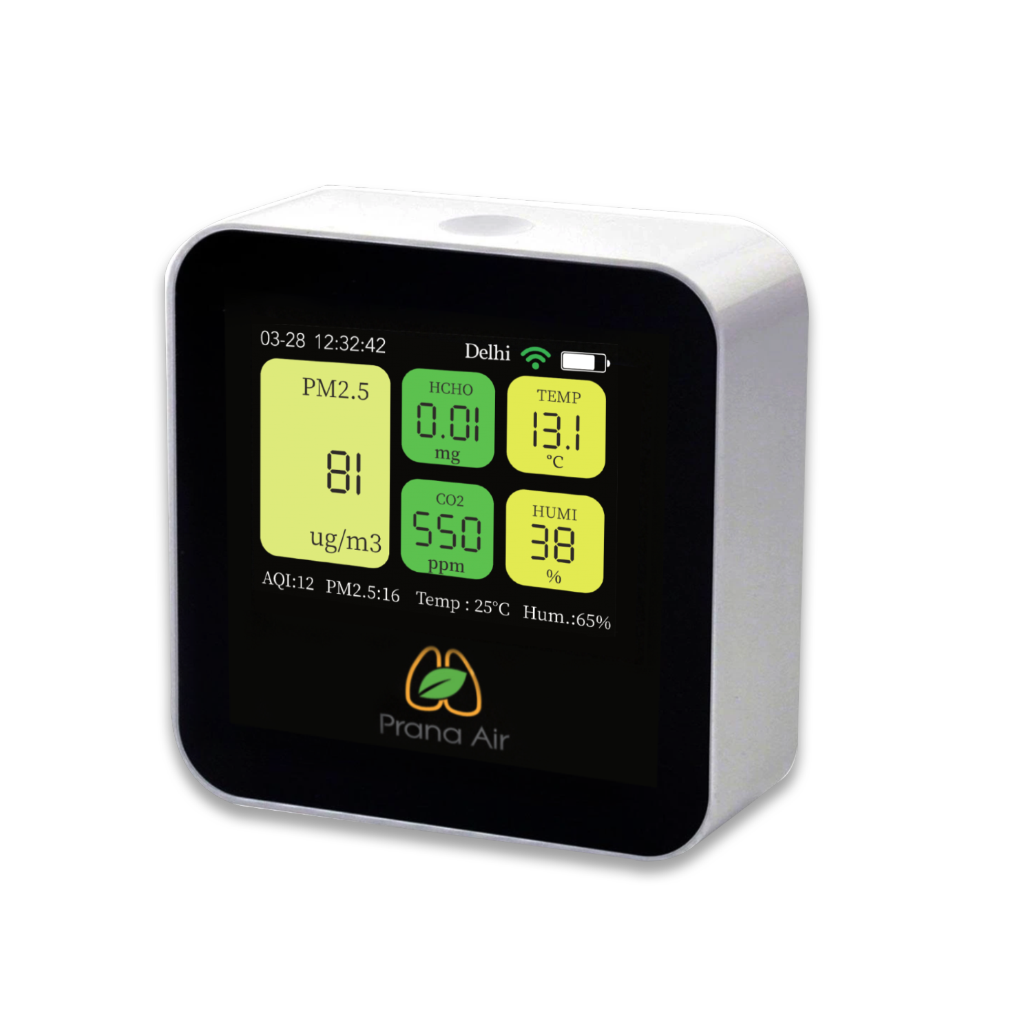
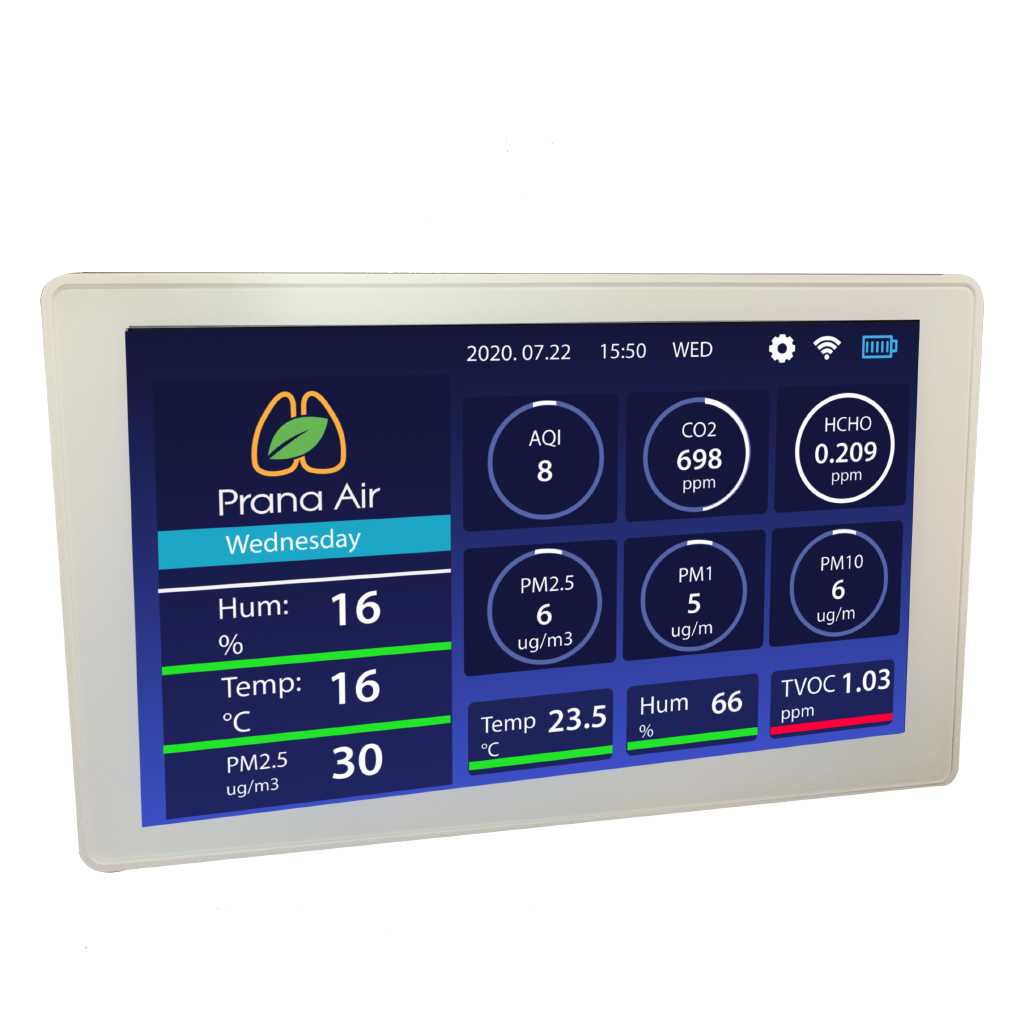
- Indoor air quality monitors and sensors –
are essential tools for monitoring the quality of the air in a home. These devices can detect and measure various pollutants such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), carbon dioxide (CO2), particulate matter, and even radon gas. They provide real-time data on the levels of these pollutants, allowing homeowners to take immediate action if necessary. Additionally, some indoor air quality monitors can also track temperature, humidity, and even noise levels, providing a comprehensive picture of the indoor environment.
- Air purifiers and filters –
Another way to improve indoor air quality is by using air purifiers and filters. These devices are designed to remove contaminants and allergens from the air, such as dust, pet dander, pollen, and mold spores. Air purifiers work by pulling air through a series of filters that trap and capture these particles, effectively cleaning the air in the process. Some air purifiers also use additional technologies like UV light or ionization to further purify the air by killing bacteria and neutralizing odors. By using air purifiers and filters, homeowners can greatly reduce the presence of airborne pollutants and improve



