- TB Enterprise - Place Where Ideas Convert Into Creation.
- +91-9067176874
- info@tbenterprise.in
Electrical thermography
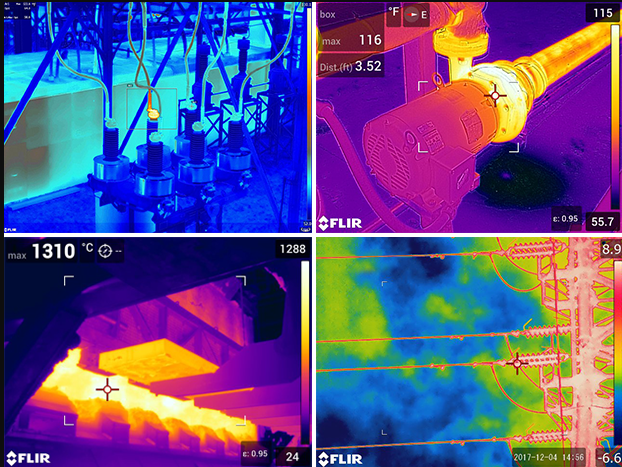
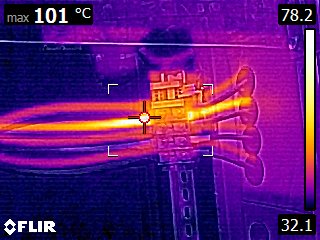
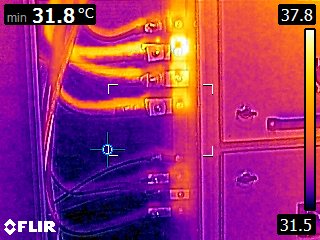
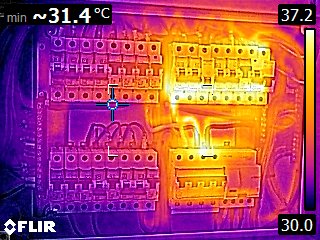
Electrical thermography is a non-destructive test method that uses infrared cameras to detect and measure temperature differences in electrical systems. Thermography can be used to:
Electrical Thermography – a non-destructive testing method that uses infrared imaging to detect and analyze thermal patterns in electrical systems. This technique allows for the identification of potential issues such as overheating components, loose connections, and faulty insulation. By capturing and analyzing thermal images, electrical thermography helps to prevent electrical failures, minimize downtime, and ensure the safety and efficiency of electrical systems.
- Importance and applications of electrical thermography – Electrical thermography plays a crucial role in various industries, including manufacturing, power generation, and building maintenance. It is used for preventive maintenance to identify and rectify potential problems before they escalate into major failures. This proactive approach helps to reduce repair costs and extend the lifespan of electrical equipment. Additionally, electrical thermography is utilized during the commissioning process to ensure that new electrical installations are functioning properly and meeting safety standards. Furthermore, this technique is essential in troubleshooting electrical systems, as it allows technicians to pinpoint the exact location of issues without the need for invasive and time-consuming methods.
- Detect poor connections, unbalanced loads, and deteriorated insulation
- Identify areas that are too hot or too cold
- Optimize maintenance programs
- Prevent costly downtime
- Enhance safety
- Lower maintenance costs
- Extend the life of production machinery

Explanation of infrared radiation and its relation to temperature measurement –
Thermography plays a crucial role in maintaining the safety and efficiency of electrical systems. Infrared radiation, which is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero, is the basis for this technology. By measuring the intensity of infrared radiation, electrical thermography can accurately determine the temperature of various components within an electrical system. This information is invaluable for identifying potential hotspots, which can indicate areas of excessive heat buildup and potential failure.
- Introduction to the concept of emissivity and its significance in electrical thermography – Emissivity, a key factor in electrical thermography, refers to the ability of an object to emit infrared radiation. It is a dimensionless value between 0 and 1, with higher values indicating greater emissivity. Understanding the concept of emissivity is crucial in accurately measuring temperatures using electrical thermography.
Benefits and Limitations of Electrical Thermography – Electrical thermography offers numerous benefits in various applications. One of the main advantages is its non-contact nature, allowing for safe and efficient temperature measurements without the need for physical contact with the object being tested. This is particularly useful in electrical systems where live wires and high voltages are present. Additionally, electrical thermography provides real-time monitoring capabilities, enabling the detection of potential faults or anomalies before they escalate into major failures.
Advantages of using electrical thermography for preventive maintenance
include increased safety for maintenance personnel, reduced downtime and costs associated with equipment failures, and improved overall system reliability. By using electrical thermography as part of a preventive maintenance programme, potential issues can be identified and addressed proactively, minimising the risk of unexpected breakdowns and disruptions to operations. This can result in significant cost savings, as unplanned downtime can be extremely costly in terms of lost production, repairs, and potential damage to other equipment.
Applications of Electrical Thermography in Various Industries
Electrical thermography has proven to be a valuable tool in a wide range of industries, providing valuable insights and benefits across different sectors. In the manufacturing industry, for example, electrical thermography can be used to detect hot spots in electrical systems, such as motors, transformers, and control panels. This early detection allows for timely maintenance and repairs, preventing costly equipment failures and production delays. Similarly, in the energy sector, electrical thermography is used to identify potential issues in power distribution systems, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of power plants and electrical grids.
Electrical maintenance in power generation plants
is crucial for maintaining the reliability and functionality of the equipment. Electrical thermography plays a vital role in this maintenance process by providing a non-invasive method to identify any abnormal heat patterns or electrical faults that may be occurring within the power generation system. By using thermal imaging cameras, technicians can easily detect overheating components, loose connections, and other potential issues that could lead to equipment malfunctions or even catastrophic failures. This proactive approach allows for timely repairs or replacements to be made, minimising downtime and maximising the overall efficiency of the power generation plant.
Thermographic inspections in manufacturing and industrial facilities
Thermographic inspections are not only valuable in power generation systems, but they also play a crucial role in manufacturing and industrial facilities. These inspections involve the use of thermal imaging cameras to identify potential problems and inefficiencies within the equipment and machinery used in these facilities. By conducting regular thermographic inspections, technicians can detect issues such as faulty insulation, motor overheating, and electrical faults that could lead to equipment breakdowns or safety hazards. This proactive approach allows for prompt repairs or maintenance to be carried out, ensuring the smooth operation of the manufacturing or industrial facility and preventing costly downtime.
Utilization of electrical thermography in building inspections and energy audits
is another valuable application of thermographic technology. By using infrared cameras, inspectors can identify areas of energy loss, such as air leaks, poorly insulated walls, or faulty HVAC systems. This information can then be used to make energy-saving recommendations and improvements, ultimately reducing energy consumption and lowering utility costs for the building owner. Additionally, electrical thermography can help identify potential fire hazards, such as overloaded circuits or loose electrical connections, allowing for timely repairs and preventing potential disasters. Overall, the utilisation of electrical thermography in building inspections and energy audits is a crucial tool in ensuring efficiency, safety, and sustainability..



